Advanced delivery systems that overcome biological barriers while maintaining safety and efficacy are essential for the success of mRNA-based therapies. Creative Biolabs integrate recent advancements and challenges facing mRNA delivery systems into a table which they analyze in depth to provide you with insights into mRNA delivery vehicles.
Comparative Analysis of mRNA Delivery Technologies
| Technology | Key Components | Mechanism of Action | Advantages | Challenges | 2023–2024 Breakthroughs | Future Directions |
| Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) | Ionizable lipids, cholesterol, PEG-lipids, phospholipids | – Ionizable lipids protonate in acidic endosomes, destabilizing membranes for mRNA release. – PEG-lipids enhance stability and reduce immune recognition. |
– High encapsulation efficiency (>90%). – Scalable manufacturing. – Proven success in vaccines. |
– Liver-dominated biodistribution. – PEG may trigger hypersensitivity. – Limited targeting beyond hepatic tissues. |
– Zwitterionic LNPs: Reduce cytokine storms by balancing surface charge (Science Advances, 2023). – ApoE-mimetic peptides: Redirect LNPs to lungs/heart (Nature Biotechnology, 2024). |
– Ligand-conjugated LNPs (e.g., transferrin for tumors). – Plant-derived lipids for sustainability. |
| Polymer-Based Carriers | Cationic polymers (PEI, PBAEs), biodegradable polyesters | – Electrostatic binding with mRNA. – pH/redox-responsive polymers release mRNA in specific cellular compartments. |
– Tunable degradation rates. – Low-cost production. – Stimuli-responsive designs. |
– High charge density causes cytotoxicity. – Batch-to-batch variability. |
– PLGA-PEG hybrids: Achieve 72-hour sustained mRNA release in tumors (Nano Letters, 2024). – Chitosan derivatives: Enhance mucosal delivery for inhaled vaccines. |
– AI-optimized polymer libraries. – Co-delivery with siRNA for combination therapies. |
| Inorganic Nanoparticles | Silica, gold, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) | – Porous structures encapsulate mRNA. – Surface functionalization enables targeting (e.g., antibodies). |
– Excellent thermal/chemical stability. – Controlled release profiles. |
– Potential long-term toxicity. – Complex clearance pathways. |
– MOF-based carriers: Deliver mRNA to brain cells with 95% efficiency (Nature Nanotechnology, 2024). – Silica-mRNA hybrids: Stabilize mRNA at room temperature for 6 months. |
– Biodegradable silica frameworks. – Integration with imaging agents for theranostics. |
| Exosomes | Natural extracellular vesicles (30–150 nm) | – Innate homing abilities via surface proteins (e.g., tetraspanins). – Membrane fusion for cytoplasmic delivery. |
– Low immunogenicity. – Cross biological barriers (e.g., blood-brain barrier). |
– Low yield in production. – Heterogeneity in vesicle size/content. |
– Engineered exosomes: Display CD47 to evade phagocytosis (Cell, 2023). – Plant-derived exosomes: Scalable production from ginger/grapefruit. |
– Gene-edited exosomes for precision targeting. – Hybrid exosome-LNP systems. |
| Hybrid Systems | Lipid-polymer hybrids, cell-membrane-coated NPs | – Combine structural stability (polymer core) with biocompatibility (lipid shell). – Camouflage with cell membranes to evade immunity. |
– Synergistic benefits of multiple materials. – Enhanced tumor accumulation. |
– Complex manufacturing. – Limited clinical validation. |
– Erythrocyte-coated LNPs: Double tumor mRNA delivery efficiency (ACS Nano, 2023). – DNA origami-LNPs: Enable programmable cargo release. |
– Multi-stimuli-responsive hybrids (pH + enzyme activation). – Autologous patient-specific coatings. |
In-Depth Analysis of Key Technologies
1. Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs): The Gold Standard
LNPs remain the most clinically advanced platform, exemplified by their role in COVID-19 vaccines. Their ionizable lipids, such as SM-102 and ALC-0315, are critical for endosomal escape—a process where the lipid bilayer fuses with endosomal membranes under acidic conditions, releasing mRNA into the cytoplasm. However, their tendency to accumulate in the liver (due to ApoE-mediated uptake by hepatocytes) limits applications for non-hepatic diseases. Recent breakthroughs include:
- Zwitterionic Lipids: These lipids, bearing both positive and negative charges, reduce interactions with immune cells. A 2023 study showed zwitterionic LNPs reduced IL-6 levels by 60% in mice compared to conventional LNPs.
- Organ-Redirecting Peptides: By attaching apolipoprotein E-mimetic peptides, LNPs can be redirected to the lungs or heart, opening avenues for treating pulmonary hypertension or myocardial diseases.
2. Polymer-Based Carriers: Balancing Efficiency and Safety
Cationic polymers like polyethyleneimine (PEI) condense mRNA into compact nanoparticles but suffer from cytotoxicity due to their high positive charge. Innovations focus on biodegradable alternatives:
- Poly(beta-amino esters) (PBAEs): These pH-sensitive polymers degrade in endosomes, releasing mRNA while minimizing toxicity. A 2024 trial demonstrated PBAE-based carriers achieved 50% higher tumor mRNA expression than LNPs in melanoma models.
- Chitosan Derivatives: Modified with hydrophobic groups, chitosan carriers enhance stability and enable mucosal delivery, critical for nasal or oral mRNA vaccines.
3. Inorganic Nanoparticles: Stability Meets Functionality
Due to their unmatched stability properties silica and gold nanoparticles become suitable for usage in extreme conditions. Silica-mRNA hybrids maintained 90% of their activity after six months of storage at room temperature which helps solve cold-chain storage issues. However, their long-term biocompatibility remains under scrutiny. The porous structures of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) enable precise mRNA loading and simultaneous delivery of adjuvants. The 2024 MOF-based delivery system transported mRNA to neurons at 95% efficiency which demonstrates its ability to treat neurodegenerative diseases.
4. Exosomes: Nature’s Delivery Vehicles
Cells naturally produce exosomes that demonstrate strong biocompatibility and precise targeting abilities. Exosomes engineered with CD47 surface markers avoid macrophage clearance and achieve twice the normal circulation time in living organisms. Extracted from ginger and grapefruit plant sources exosomes provide an economical and scalable substitute but remain poorly understood in terms of their functioning mechanisms.
5. Hybrid Systems: Bridging Material Advantages
Combining lipids with polymers or inorganic cores addresses individual material limitations. For example, lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles (LPNs) use a PLGA core for controlled release and a lipid shell for enhanced cellular uptake. Erythrocyte membrane-coated LNPs leverage natural cell adhesion molecules to improve tumor targeting, achieving a 2-fold increase in mRNA delivery to lung metastases in preclinical models.
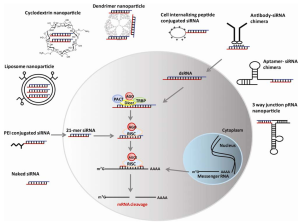
Figure.1 The mechanism and delivery strategies for RNA interference.2
Overcoming Challenges: From Bench to Bedside2Improving Targeting Precision
- Active Targeting: Conjugation of ligands (e.g., folate, HER2 antibodies) to LNPs enhances uptake in specific cells. A 2023 study showed folate-functionalized LNPs increased mRNA delivery to ovarian tumors by 70%.
- Passive Targeting: Nanoparticles >10 nm accumulate in tumors via the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect, but variability in human EPR limits reliability.
- Enhancing Stability and Scalability
- Lyophilization Advances: Trehalose-based cryoprotectants preserve mRNA integrity during freeze-drying. Spray-drying techniques reduce production time by 40% compared to traditional methods.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: Algae-derived lipids (e.g., squalene) and bioengineered yeast platforms are emerging as eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic lipids.
- Mitigating Immunogenicity
- Nucleoside Modifications: Incorporating pseudouridine or 5-methylcytosine reduces TLR activation. Moderna’s COVID-19 vaccine uses N1-methylpseudouridine to minimize immune detection.
- Stealth Coatings: Polyglycerol or polysarcosine coatings replace PEG, avoiding anti-PEG antibody responses observed in 40% of patients.
Future Horizons: Interdisciplinary Synergy
- AI and Machine Learning
AI models like AlphaFold are predicting lipid-mRNA binding affinities, accelerating the design of novel carriers. A 2024 algorithm identified a lung-targeting lipid with 80% higher efficiency than industry standards.
- Gene Editing Integration
Gene-editing mRNA delivery using biodegradable polyplexes has cured genetic liver disorders in mice, with clinical trials expected by 2025.
- Global Health Equity
Efforts to decentralize mRNA production—such as freeze-dried LNPs stable at 25°C—aim to democratize access to low-resource regions.
Conclusion
The future of mRNA delivery lies in a diversified toolkit: LNPs for rapid deployment, polymers for tunable release, exosomes for precision, and hybrids for multifunctionality. By addressing challenges in targeting, stability, and immunogenicity through interdisciplinary innovation, next-generation carriers will unlock mRNA’s potential to treat cancers, genetic disorders, and infectious diseases globally.
Advanced mRNA Delivery Solutions at Creative Biolabs
At Creative Biolabs, we provide cutting-edge mRNA delivery technologies to advance your therapeutic and vaccine development. Our comprehensive platform offers versatile solutions tailored to your specific needs. Explore our categorized delivery systems below:
Lipid-Based Delivery Systems
- Lipid-Based Vectors: Customizable lipid-based systems for efficient mRNA encapsulation and delivery.
- Lipoplex: Stable lipid-nucleic acid complexes optimized for enhanced cellular uptake.
- Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs): Precision-engineered nanoparticles for targeted mRNA delivery.
Polymer-Based Delivery Systems
- Polymer-Based Vectors: Biodegradable polymers for controlled mRNA release and reduced toxicity.
- Polyplex: Polymer-DNA/RNA complexes designed for high transfection efficiency.
- Micelleplex: Self-assembled micelles for improved stability and targeted delivery.
Hybrid & Advanced Systems
- Hybrid Vectors: Integrate lipid-polymer hybrids for enhanced stability and delivery efficiency.
- Lipopolyplex: Combines lipids and polymers for superior mRNA protection and delivery.
- Cationic Nanoemulsion: Charge-modified emulsions for mucosal and systemic mRNA delivery.
Why Partner With Us?
- Tailored Solutions: Customizable platforms for vaccines, therapeutics, and gene editing.
- GMP Compliance: Scalable production under stringent quality controls.
- End-to-End Support: From design to in vivo validation.
Reference
- Kowalski, P.S.; Rudra, A.; Miao, L.; Anderson, D.G. Delivering the messenger: Advances in technologies for therapeutic mRNA delivery.
Molecular Therapy2019, 27 (4), 710–727.DOI: 1016/j.ymthe.2019.02.012 - Zhou, J.H.; Shum, K.T.; Burnett, J.C.; Rossi, J.J. Nanoparticle-Based Delivery of RNAi Therapeutics: Progress and Challenges. Pharmaceuticals2013, 6 (1), 85–106. DOI: 3390/ph6010085. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 3.0, without modification.
